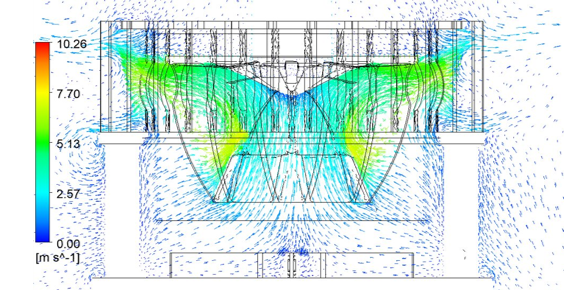
When parts are new the slurry flow entering the cell is efficiently pumped through the impeller. The impeller disperses air and provokes turbulence into the slurry and causes particles and bubbles to collide and adhere. It also produces internal flow patterns in the cell to allow the bubbles to rise through the slurry. In the CFD studies, the evident wear on the rotor and stator was seen to weaken the ability to perform key functionalities needed for efficient flotation.
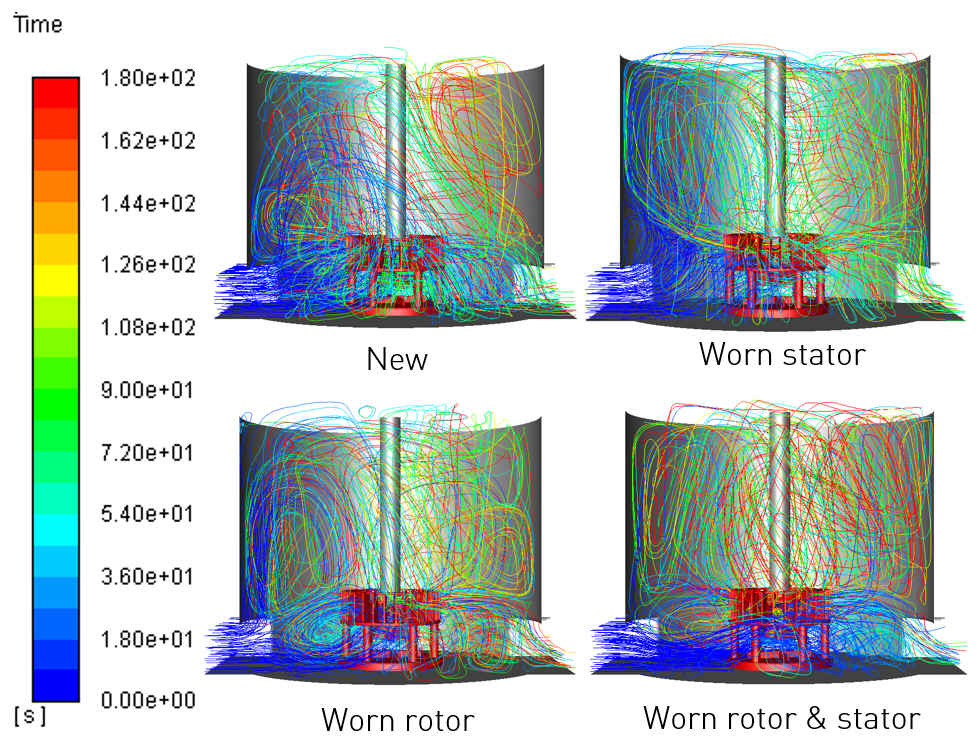
CFD results - particle time path lines (side view)
When a rotor is worn, power intake for the mechanism drops and the streams outwards from the impeller become smoother. This causes heavier particles to remain on the floor and pulp aeration also becomes less uniform. As the stator wears it loses some ability to resist the slurry flow, meaning less turbulence, and fewer opportunities for bubbles and particles to collide and attach. When both parts are worn, the power drop is enhanced.
With high wear rates the risk of short-circuiting, i.e. feed slurry leaving the cell without circulating through the impeller, increases. The CFD short-circuiting was seen at the bottom of the cell and under the impeller.
Summary
|
Rotor wear |
Stator wear |
|
Less power draw, pumping |
Less mixing and turbulence |
|
Less gas dispersion |
Alters cell internal flows |
|
Risk of short-circuiting new feed |
Less bubble-particle collision |
|
Flotation performance loss |
Flotation performance loss |
Conclusions
Wear of the mixing mechanism can have a negative effect on flotation performance as studied. Wearing is gradual and depends on pulp characteristics and rotation speed. To maintain performance, rotors and stators should be regularly inspected and kept in good condition.
Metso Outotec can provide support for evaluating the condition of the mechanism by supplying wear limit drawings and recommendations for Metso Outotec FloatForce and SkimForce mechanisms.