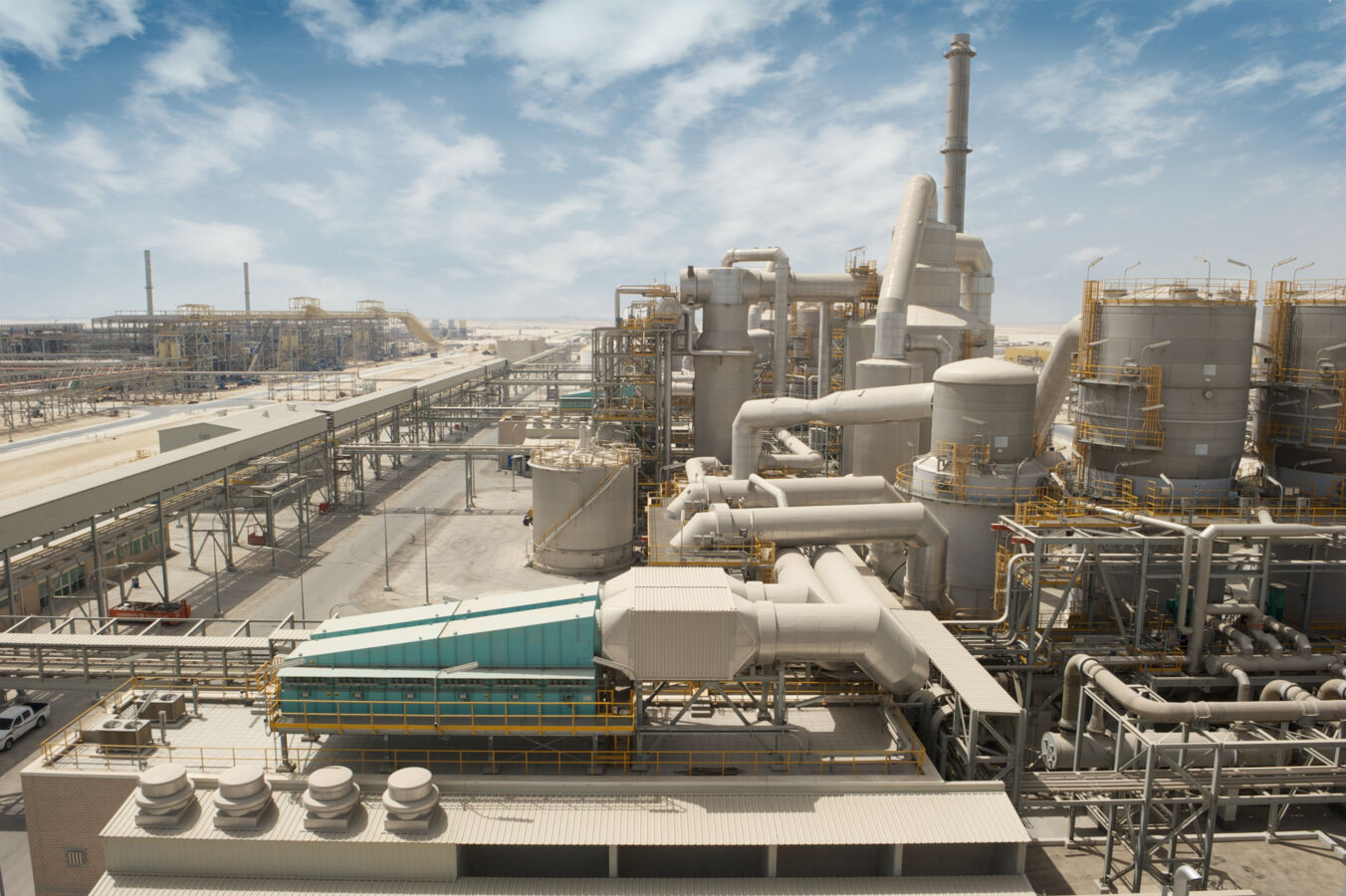
Digitization, less commonly digitalization, is the process of converting information into a digital (i.e. computer-readable) format. Digitizing simply means the conversion of analog source material into a numerical format; the decimal or any other number system that can be used instead.
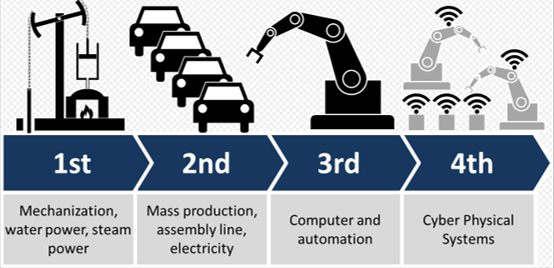
Industry 4.0 is a name for the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It includes cyber-physical systems, the Internet of things, cloud computing and cognitive computing. Industry 4.0 creates what has been called a "smart factory". Within the modular structured smart factories, cyber-physical systems monitor physical processes, create a virtual copy of the physical world and make decentralized decisions. Over the Internet of Things, cyber-physical systems communicate and cooperate with each other and with humans in real time, and via the Internet of Services, both internal and cross-organizational services are offered and used by participants of the value chain.
The term "Industrie 4.0" originates from a project in the high-tech strategy of the German government, which promotes the computerization of manufacturing. The term "Industrie 4.0" was revived in 2011 at the Hannover Fair. In October 2012 the Working Group on Industry 4.0 presented a set of Industry 4.0 implementation recommendations to the German federal government. The Industry 4.0 workgroup members are recognized as the founding fathers and driving force behind Industry 4.0.
The object of this paper is to consider the implications of Industry 4.0 on the future design/operation and maintenance of an autonomous acid plant.