Click here to access our first webinar, which focuses on the Factors to consider when investing into a new e-Scrap smelter. This part two discusses the flowsheet process and gas cleaning more in-depth.
Main steps and considerations in setting up a flowsheet for treating e-Scrap
Building a flowsheet for treating e-scrap can be a complex task, but luckily the key steps are quite general.
The first step in e-scrap flowsheet development is to understand the feed. E-scrap can come in many forms, and the feed should have a sufficient description to help us interpret the accompanying analysis. With sufficient information, we can turn the elemental analysis into a more useful component analysis.
For the purposes of setting up a flowsheet, you can make some assumptions on missing information, but large amounts of unknown material in the feed could lead to a suboptimal solution. Therefore, understanding the feed is key. E-Scrap is a challenging feed source, and its composition and supply are constantly evolving, potentially on a batch-by-batch basis. Ideally, you want a process that has flexibility to accommodate variations in feed. Generally, feeds that are similar will be grouped. Should there be any higher grade material, it may be that it can be fed separately into downstream processes, so as to minimize losses in early processing steps.
The final key piece of information in setting up a flowsheet is the desired product. An existing smelter may be able to feed a black copper into an existing converting process, but a new greenfield site may be looking to produce a refined copper product. Naturally, the more processing required, the more complex the flowsheet can become.
Steps in flowsheet building
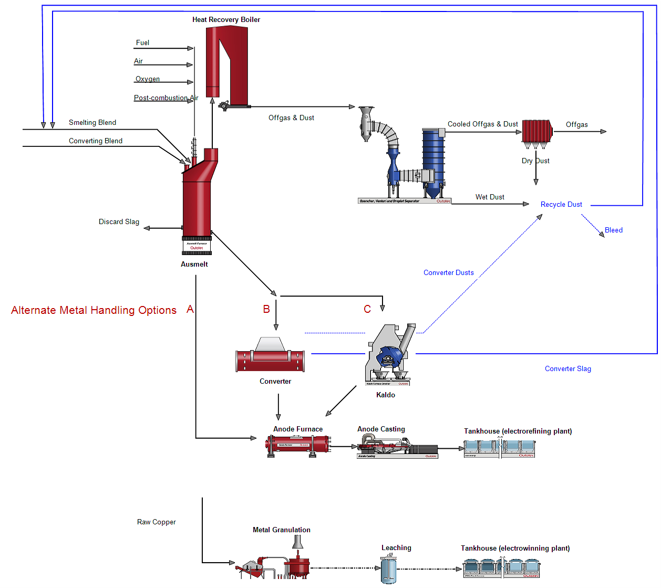
Once we understand our feed, the capacity and desired end product, we can start to set up a flowsheet. For those of you who attended webinar 1 in the series, we discussed two key Metso Outotec technologies for smelting of eScrap - the Ausmelt process and the Kaldo process. Each has particular strengths, so the best unit can be applied on a case-by-case basis.