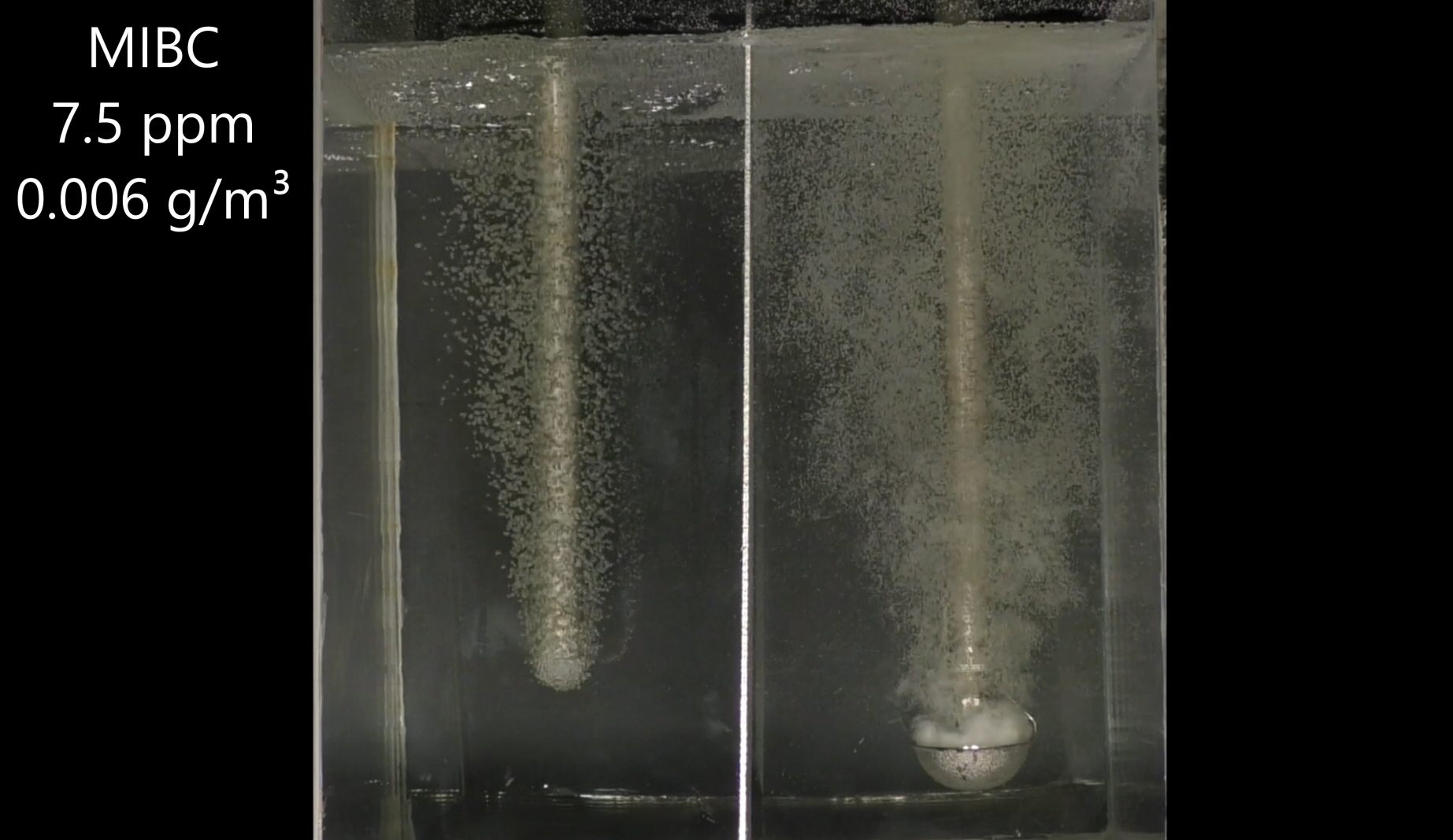
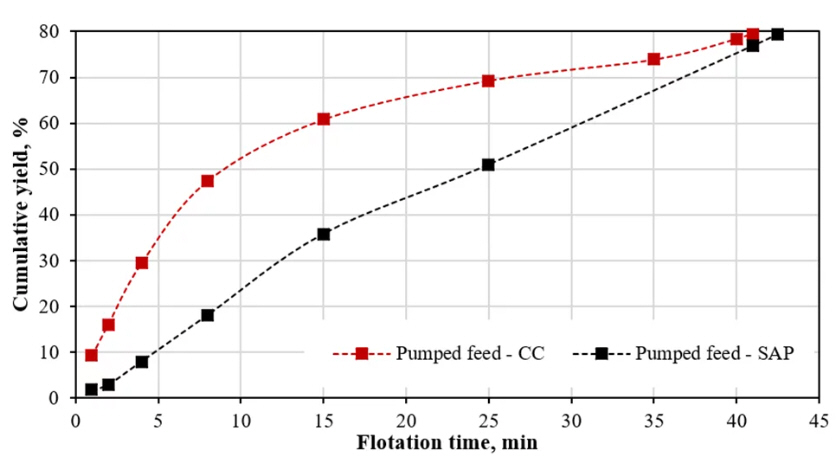
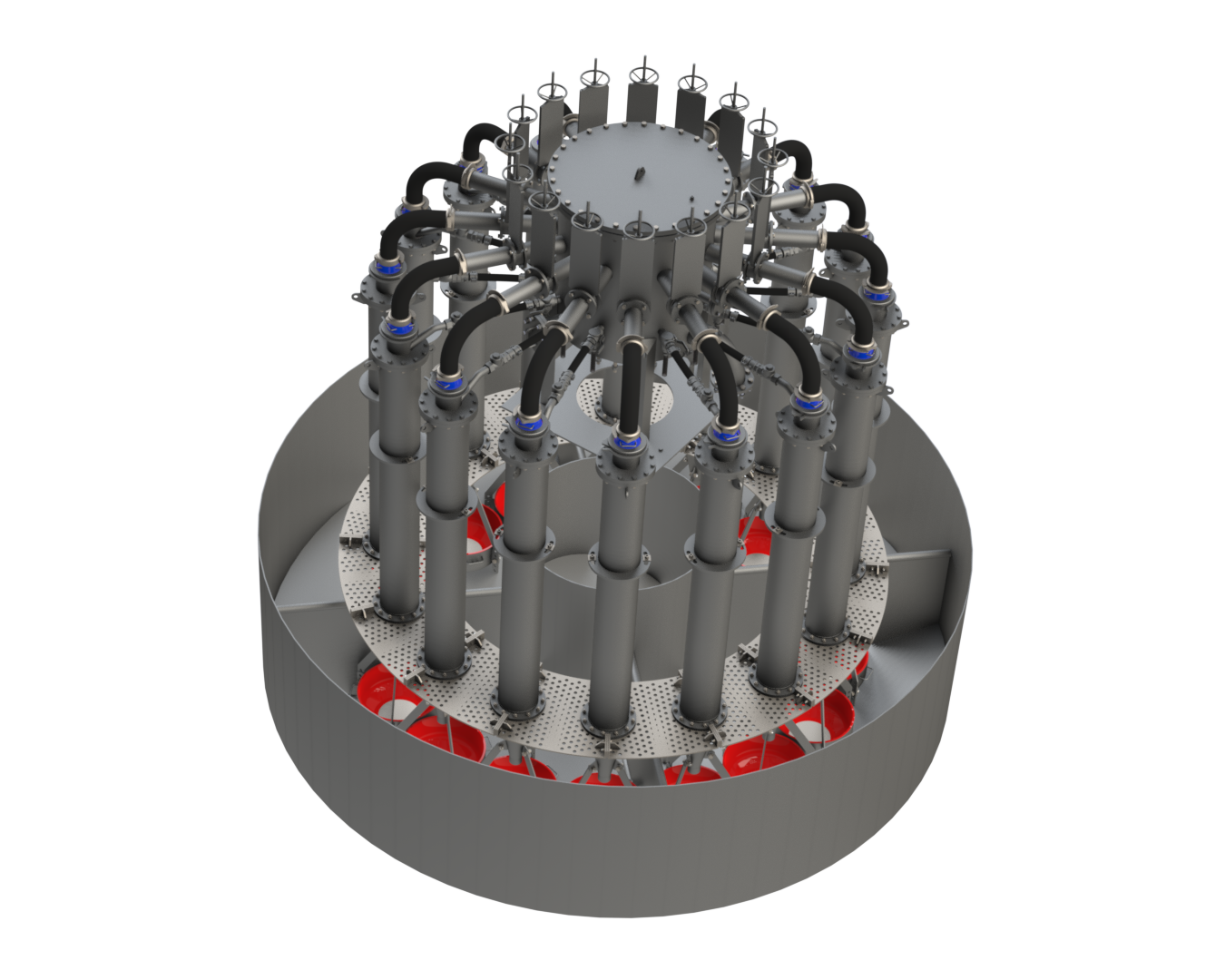
The emergence of pneumatic flotation technology has revolutionized mineral processing, offering a more efficient and effective approach to separating valuable minerals from gangue. These cells utilize forced air and slurry mixtures at high velocities to create bubbles, eliminating the need for mechanical agitation. One of the key advantages of this method is its ability to not only reduce energy consumption but also to improve the quality of the froth and increase flotation rates, especially for fine particles. This evolution reflects a broader trend in mineral processing, where continual technological advancements are pursued to optimize operations and address the dynamic demands of the market.
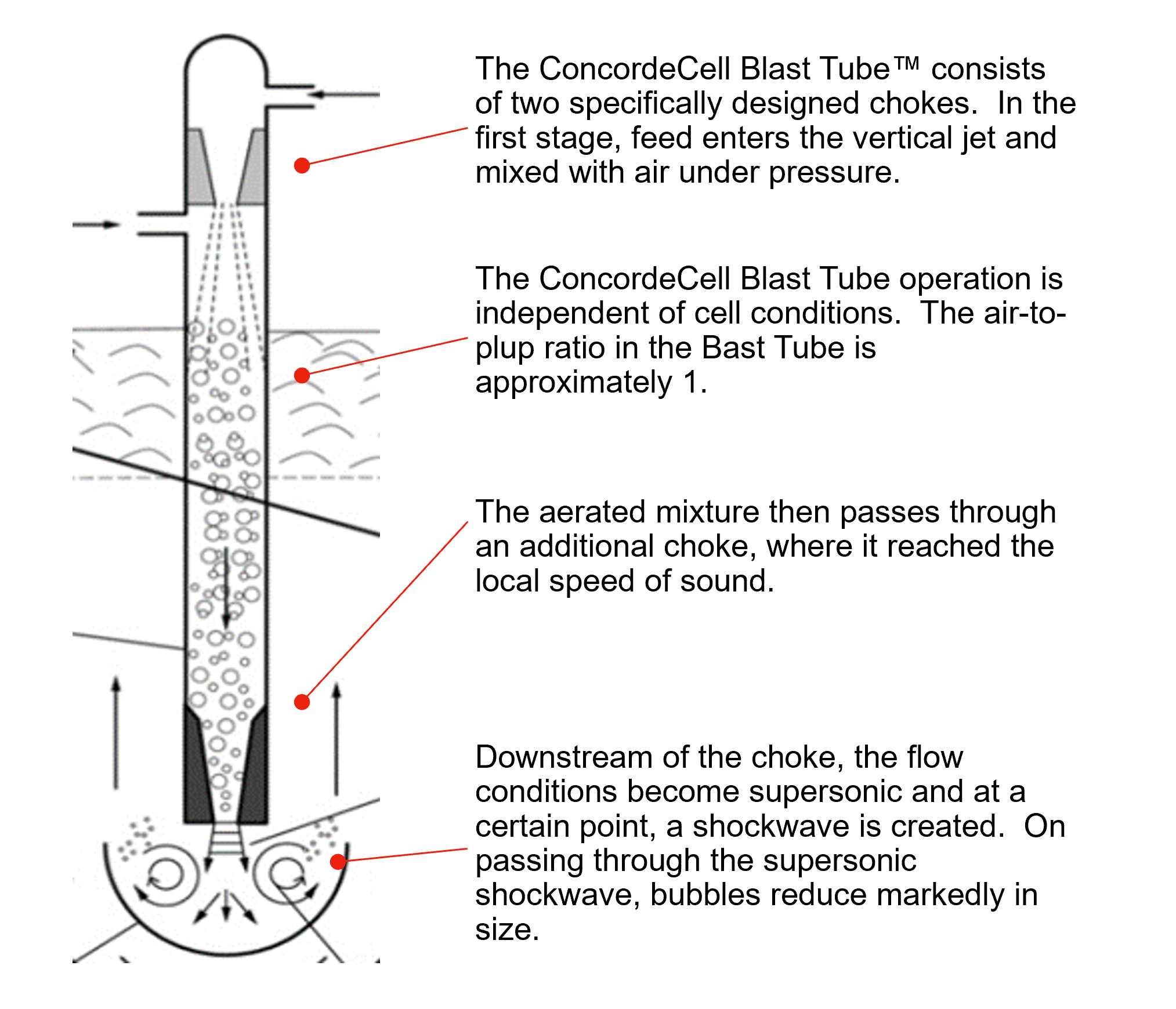
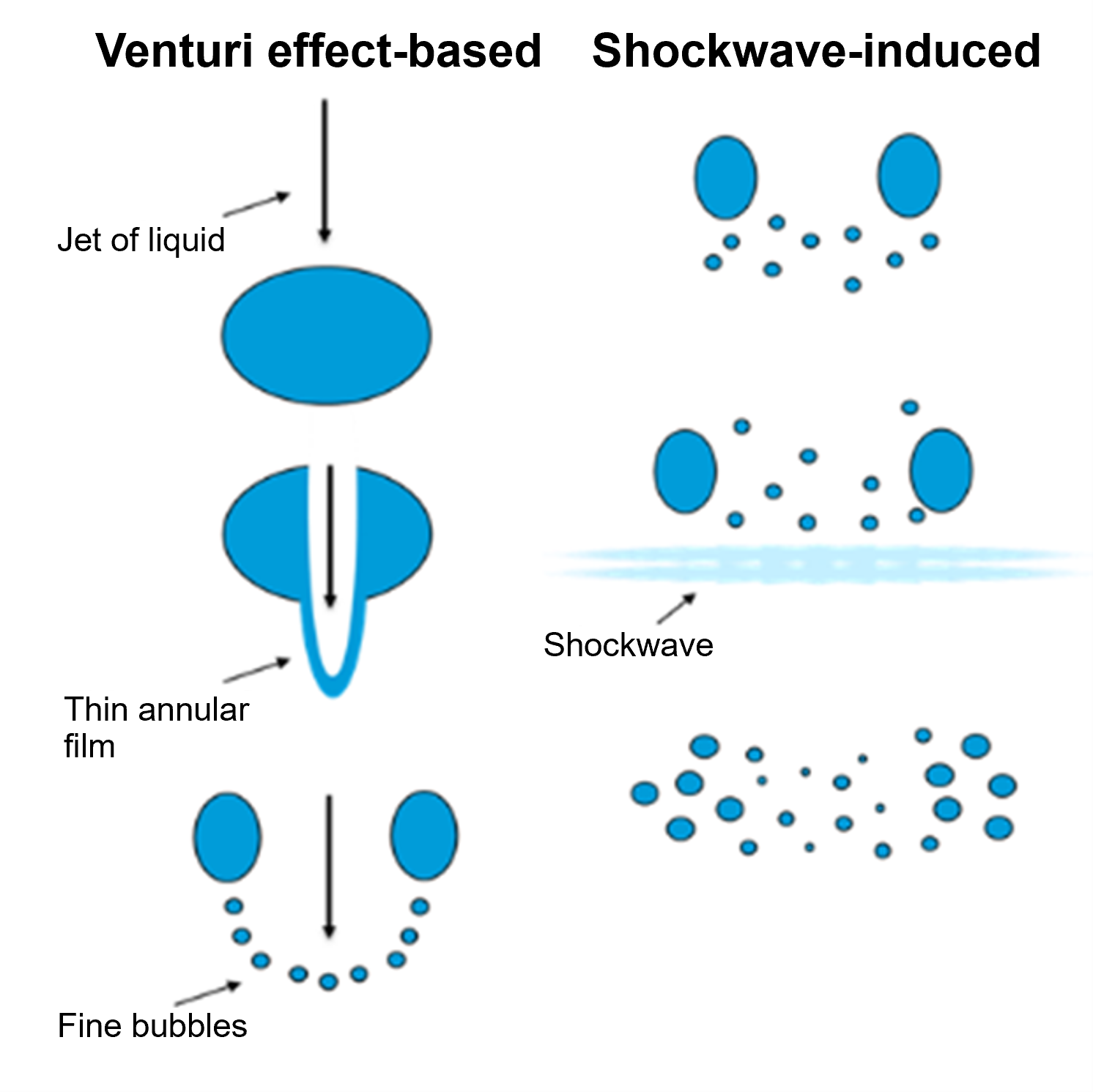
The transition to pneumatic flotation cells revolutionized mineral processing. The advent of self-aspirated pneumatic flotation cells introduced innovative approaches, such as vertical columns or downcomers, which dispersed air and pulp into dense froths of bubbles. Despite being a novel technology, demands for finer bubble generation with larger fluxes and enhanced operational control over air-to-pulp ratios (APR) persisted, driving further innovations.
Industry demands and trends
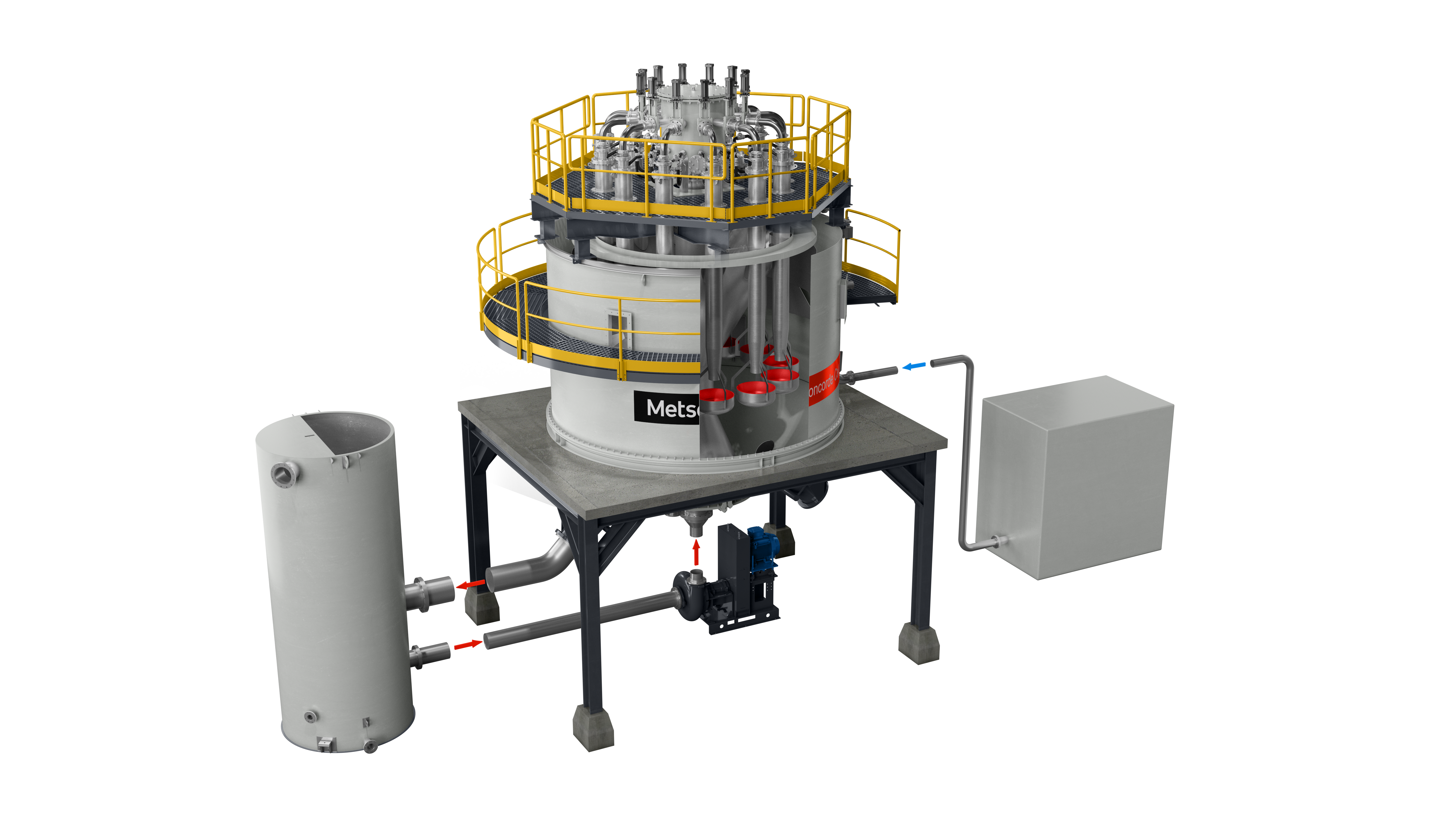
In response to evolving industry needs, upgrading existing flotation technology has emerged as a cost-effective solution. Modern upgrades, like the Concorde Blast Tube™ upgrade for self-aspirated pneumatic flotation cells, offer several advantages. They enhance performance while minimizing additional capital expenditure and space requirements. These upgrades address challenges posed by complex ore bodies, provide operational flexibility, and ensure rapid returns on investment, aligning with the dynamic nature of the market.
The push for upgrading flotation technology is underpinned by several pivotal factors, each contributing to the industry's pursuit of enhanced efficiency and competitiveness:
Cost-effectiveness: Upgrades present a financially practical path to improving performance without the hefty investment associated with new installations. By optimizing existing equipment, operations stand to boost their recovery rates and throughput, thereby bolstering profitability without breaking the bank.
Reduced footprint: Modern upgrades, exemplified by innovations like the Concorde blast tube for self-aspirated pneumatic flotation cells, are designed to seamlessly integrate into current flotation setups. This design ethos minimizes the need for additional space, offering a benefit to operations grappling with spatial limitations imposed by environmental regulations or other constraints.
Meeting modern ore challenges: With ore bodies evolving to become increasingly complex and lower in grade, the efficacy of traditional flotation technology wanes. Upgrades incorporating cutting-edge aeration and bubble generation techniques rise to this challenge, ensuring competitive recovery rates in the face of these demanding ore types.
Operational flexibility: Upgrades often bundle advanced control systems and automation features, affording operators greater flexibility and precision in managing flotation processes. This adaptability proves invaluable for navigating variations in ore quality and composition, ensuring consistent performance amidst changing operational landscapes.
Quick Implementation and ROI: Upgrading existing systems typically offers quicker implementation timelines compared to constructing entirely new facilities. This swift turnaround translates to faster returns on investment, a critical advantage in a dynamic market characterized by fluctuating mineral prices and demand.
These driving forces underscore the imperative for continuous innovation and improvement in flotation technology, enabling mineral processing operations to stay ahead in an ever-evolving landscape.